Assessing Your Current E-commerce Platform's Capabilities
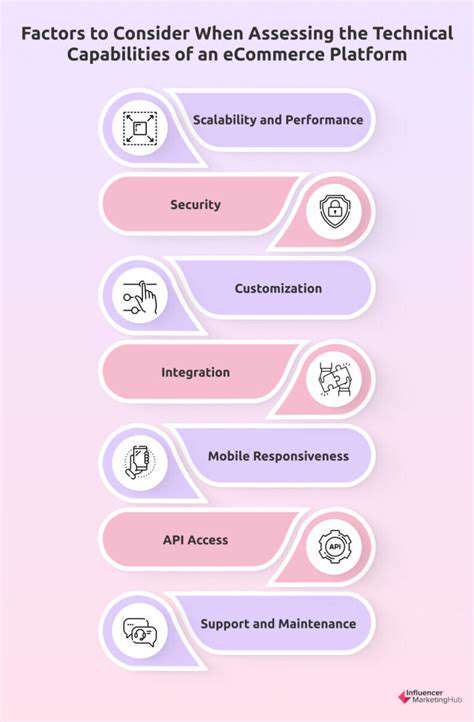
Understanding Your Current Platform
Before making any changes to your online store, it's essential to take a deep dive into how your current e-commerce platform operates. Many business owners overlook this critical evaluation phase, jumping straight into upgrades without fully grasping their system's capabilities. The most successful online retailers spend significant time analyzing their platform's strengths and weaknesses before making changes. This careful examination should cover both backend functionality and customer-facing features.
When reviewing your platform, create a detailed checklist of essential features. Does your system support the payment methods your customers prefer? Can it handle seasonal traffic spikes without crashing? These operational questions often reveal surprising gaps. Platform limitations that seem minor today can become major obstacles as your business grows. Documenting these constraints now prevents costly surprises later.
Analyzing Sales and Customer Data
Your sales records tell a story far beyond simple revenue numbers. Savvy merchants examine patterns in purchase timing, product combinations, and abandonment rates. These metrics reveal hidden opportunities - perhaps certain products sell better on weekends, or customers frequently abandon carts at a specific checkout step. Data doesn't lie, and these numerical insights often contradict our assumptions about customer behavior.
Customer profiles deserve equal attention. Beyond basic demographics, study how different segments interact with your site. Do mobile users purchase different items than desktop visitors? Are repeat buyers coming from specific marketing channels? This granular understanding transforms generic marketing into targeted campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups. Regularly updating these customer personas keeps your strategies aligned with actual shopper behavior.
Evaluating Website Performance
Site speed impacts more than user satisfaction - it directly affects your search rankings and conversion rates. Modern shoppers expect pages to load instantly, with 53% abandoning sites that take longer than three seconds to load. Test your site's performance across devices and connection speeds, paying special attention to image-heavy product pages. Mobile performance deserves particular scrutiny, as over 60% of e-commerce traffic now comes from smartphones.
Security evaluations should extend beyond basic SSL certificates. Regular vulnerability scans, payment system audits, and compliance checks protect both your business and customers. The visual design should facilitate effortless navigation while reinforcing brand identity. Confusing layouts or inconsistent branding create subconscious distrust that drives customers away.
Assessing Marketing and Promotion Strategies
Effective marketing requires constant measurement and adjustment. Track which campaigns generate not just clicks, but qualified leads that convert to sales. Many businesses discover they're investing heavily in channels that attract window-shoppers rather than serious buyers. The most valuable marketing metrics often aren't the most obvious - sometimes smaller, highly targeted campaigns outperform broad initiatives.
Seasonal trends significantly impact promotional effectiveness. Analyze historical data to identify patterns - perhaps email campaigns perform better on weekday mornings, or certain product categories see spikes after specific events. Timing promotions to match these natural buying rhythms dramatically improves ROI. Don't overlook emerging platforms where your competitors haven't yet established presence.
Reviewing Your Customer Service Processes
Customer service quality differentiates thriving e-commerce businesses from struggling ones. Map the entire support journey from initial contact to resolution, identifying unnecessary steps or delays. Customers increasingly expect 24/7 availability with response times under an hour - can your current systems meet these expectations? Mystery shopping your own support channels often reveals surprising gaps between intended and actual service quality.
Support ticket analysis can uncover systemic issues before they become crises. Are certain product questions recurring? Is there a particular step in the ordering process that consistently confuses customers? Proactively addressing these pain points reduces support volume while improving customer satisfaction. Consider implementing AI chatbots for common queries while reserving human agents for complex issues.
Analyzing Competition
Competitive analysis goes beyond price comparisons. Study how competitors structure their product pages, what guarantees they offer, and how they handle returns. The most insightful discoveries often come from analyzing competitors' customer reviews - their weaknesses represent your opportunities. Pay particular attention to how industry leaders handle post-purchase engagement, as this area frequently separates top performers from average ones.
Technology adoption patterns reveal much about competitors' strategies. Are they implementing AR product previews or one-click checkout? Such innovations often signal where the market is heading. Rather than copying competitors outright, identify the strategic thinking behind their decisions to inform your own unique approach. Subscribe to competitors' newsletters and follow their social media to understand their messaging strategies.
Data Migration and Integration Strategies
Data Migration Planning and Strategy
Successful data migration begins with comprehensive discovery. Catalog all data types, from customer records to inventory logs, noting their formats and dependencies. Overlooking even minor data relationships can cause major issues post-migration. Create a phased migration plan that prioritizes business-critical data while allowing time for testing at each stage. This approach minimizes disruption while ensuring data integrity.
Stakeholder involvement proves crucial during planning. Department heads often identify essential data relationships that IT teams might miss. Regular cross-departmental meetings surface these hidden dependencies before they become problems. Document every decision and assumption - this audit trail proves invaluable when troubleshooting post-migration issues.
Data Validation and Quality Control
Data cleansing before migration saves countless hours later. Identify and resolve duplicates, standardize formats, and fill critical gaps. Many organizations discover their clean data contains surprising inconsistencies when examined closely. Implement validation rules that flag anomalies during the migration process rather than after completion.
Create sample test datasets representing various scenarios to verify migration accuracy. These should include edge cases that stress-test the system. Testing with real but non-critical data provides the most reliable validation. Schedule multiple validation checkpoints rather than relying solely on final verification.
Data Transformation and Mapping
Field mapping requires careful attention to semantic meaning beyond simple format conversion. A customer ID in one system might serve a different purpose than similarly named fields elsewhere. These conceptual differences cause more migration problems than technical format issues. Document every mapping decision with clear rationale for future reference.
Transformation rules should accommodate not just current needs but foreseeable future requirements. Overly specific transformations may need reworking sooner than anticipated. Where possible, implement flexible transformation logic that can adapt to changing business rules without requiring complete re-migration.
Data Security and Compliance
Data protection measures must extend throughout the migration lifecycle. Temporary storage locations and transfer channels often represent vulnerable points. Many data breaches occur during system transitions when security protocols lapse. Conduct thorough security assessments of all tools and platforms involved in the migration process.
Compliance requirements frequently differ between source and target systems. New platforms may require additional consent mechanisms or data handling procedures. Consult legal experts to ensure the migrated data meets all current regulatory standards, not just those governing the original system.
Integration with Existing Systems
System integration testing should occur in environments that mirror production as closely as possible. Testing in idealized conditions often misses real-world performance issues. Pay particular attention to integration points with legacy systems, as these frequently cause unexpected problems.
Develop rollback procedures for each integration phase. The ability to quickly revert changes prevents small issues from cascading into major outages. Monitor integrated systems closely during initial operation, as some issues only surface under actual usage patterns.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Maintenance
Immediate post-migration monitoring should focus on both system performance and data quality. Many data issues only become apparent when users begin working with the migrated information. Establish clear escalation paths for reporting and resolving post-migration issues.
Schedule comprehensive data audits at regular intervals following migration. Some data degradation occurs gradually and won't be caught by initial checks. User feedback provides invaluable insights into potential data quality issues that automated checks might miss.