Emphasizing Concise and Clear Input Fields

Understanding the Importance of Concise Input
Effective communication and data processing hinge on clear, straightforward input. When inputs are ambiguous or overly complex, mistakes and misunderstandings often follow, wasting time and resources. Systems function best when user input is both brief and unambiguous. This method guarantees that data remains easy to interpret and immediately actionable.
Input formats should be designed for simplicity, stripping away any unnecessary elements. Not only does this accelerate processing, but it also cuts down on human errors. Whether for everyday transactions or advanced research, streamlined input is indispensable.
Strategies for Achieving Concise Input
Precision in language is key. Use the fewest words needed to communicate your point clearly. Unless your audience is technical, avoid jargon and opt for plain language with well-defined terms.
Standardized formats are another powerful tool. They ensure uniformity, simplifying data interpretation for both humans and machines. Consistency minimizes confusion and reduces discrepancies.
Minimizing Redundancy in Input Fields
Duplicate or unnecessary fields create frustration and inefficiency. Review each input field critically, removing those that serve no purpose or repeat existing data. Trimming redundancy improves both system performance and user satisfaction by eliminating cognitive overload.
Validating Input for Accuracy and Completeness
Catching errors at the input stage prevents bigger problems later. Implement strict validation protocols to block incomplete or incorrect data from entering the system. This step is non-negotiable for maintaining trustworthy data and avoiding expensive corrections.
Ensuring User-Friendliness and Accessibility
Input interfaces must be intuitive. Labels should be explicit, navigation effortless, and the design inclusive for all users. A well-crafted interface reduces mistakes by minimizing confusion and frustration. Adding helpful hints or examples directly in the form can further clarify expectations without requiring external help.
Leveraging Mobile-Specific Design Principles
Optimizing User Experience
With mobile devices dominating daily life, designs must cater to their unique limitations. Mobile-first design focuses on simplicity, easing navigation to reduce mental strain. Factors like screen dimensions, touch responsiveness, and data usage demand careful attention to create intuitive interactions.
Small screens require prioritization—highlight key actions and trim excess content. This precision boosts engagement while lowering abandonment rates.
Responsive Design for Seamless Transitions
A single adaptable layout eliminates the need for separate versions. Content rearranges dynamically to fit any device, preserving functionality and aesthetics.
This flexibility strengthens brand perception by delivering reliability across all platforms.
Intuitive Navigation for Enhanced Usability
Mobile users favor simplicity. Straightforward menus, descriptive labels, and logical content organization improve satisfaction.
Efficient navigation shortens search times, directly increasing user retention.
Leveraging Mobile-Specific Features
Capabilities like GPS, notifications, and in-app messaging enable personalized experiences. When used thoughtfully, these tools deepen user connections and add value.
Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designs must accommodate disabilities through adjustable text sizes, screen readers, and alternative controls. Accessibility isn’t just compliance—it’s ethical design.
Performance Optimization for Speedy Loading
Mobile users abandon slow sites. Compress images, streamline code, and use caching. Speed is critical—lagging interfaces drive users away instantly.
Resource efficiency ensures swift load times and smooth performance.
Understanding User Behavior and Preferences
Analytics reveal how users engage with your platform. Metrics like bounce rates and session duration pinpoint areas needing refinement, allowing data-driven design improvements.
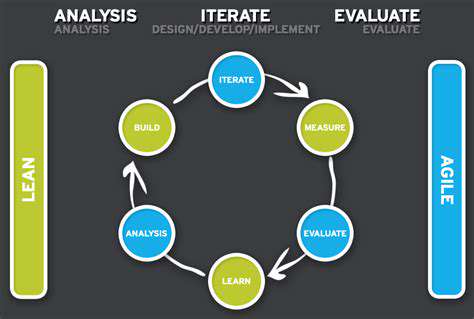
Testing and Iterating for Optimal Performance

Testing the Core Functionality
Comprehensive testing validates that all features work as intended. Test diverse scenarios—standard inputs, edge cases, and invalid data—to expose weaknesses. Early bug detection prevents costly fixes post-launch and upholds quality standards.
Vary test datasets to simulate real-world conditions. Include typical, extreme, and erroneous inputs to assess robustness. Rigorous testing is the foundation of a stable, reliable product.
Iterative Refinement and Feedback Loops
Continuous improvement cycles integrate user feedback and performance data. Regular updates address pain points and enhance usability based on actual usage patterns.
Feedback from surveys, analytics, and user tests highlights improvement areas. Data analysis drives targeted optimizations, refining the product iteratively.
Optimizing Performance and Scalability
Identify and resolve bottlenecks to maintain speed under load. Efficiency ensures consistent responsiveness regardless of user numbers or data volume. Stress-test at varying capacities to confirm stability.
Design for growth from the outset. Scalable architectures prevent performance drops as demand increases. Technology choices should support seamless expansion without sacrificing reliability.