Creating intuitive navigation means predicting user behavior and designing pathways that match their expectations. The interface should communicate its structure clearly enough that users never feel lost or confused. Visitors should instinctively understand how to move between different parts of the platform without unnecessary experimentation.
This approach to design reduces mental effort, letting users concentrate on content rather than interface mechanics. By anticipating user needs and providing clear directional cues, intuitive navigation transforms the overall interaction quality.
The Impact of Navigation on Conversion Rates
Well-executed navigation directly influences whether visitors complete desired actions. When users can locate what they need quickly, they're far more likely to make purchases, submit forms, or sign up for services. Conversely, confusing navigation leads to frustration and abandoned sessions.
A polished, intuitive navigation system dramatically decreases early exits while increasing completion rates for key actions. Strategic placement of calls-to-action and essential information forms the foundation of successful navigation planning.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Navigation Design
Navigation must accommodate all users, including those with disabilities, to be truly effective. This means using straightforward language, including descriptive text for images, and ensuring full keyboard operability. Adhering to accessibility standards doesn't just help specific groups - it improves the experience for everyone.
When designers emphasize accessibility, they create digital spaces that welcome all visitors equally. This results in broader audience reach and enhanced platform reputation.
Visual Design and Navigation: A Harmonious Partnership
Aesthetic choices profoundly affect navigation effectiveness. Consistent, appealing visual elements including color schemes, typography, and imagery contribute to intuitive wayfinding. Clear visual indicators like contrasting colors and distinctive shapes make navigation both engaging and comprehensible.
Thoughtful visual hierarchy remains essential. Highlighting critical information through size, placement, and visual prominence boosts both engagement and conversion potential.
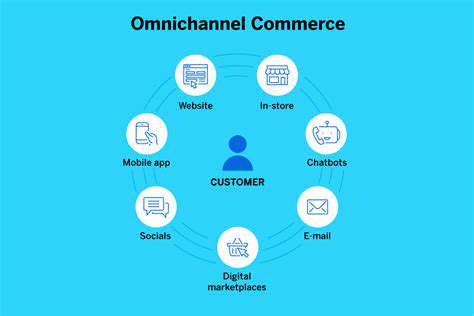
Mobile-First Navigation: Adapting to Modern Trends
With mobile devices dominating internet access, navigation must prioritize smaller screens. Digital experiences must fluidly adjust to various screen dimensions while maintaining intuitive operation. This requires navigation systems that are compact yet fully functional, often employing mobile-specific patterns like collapsible menus and touch-optimized controls.
This philosophy extends beyond technical adaptation to understanding mobile user behavior. Well-executed mobile navigation directly influences satisfaction and interaction quality.
Crafting a User-Centric Navigation Structure
Understanding User Needs in Mobile Design
Mobile users typically operate under time pressure with limited patience for complexity. Effective navigation must anticipate their immediate needs, enabling quick access to required information with minimal interaction. Identifying user intentions is critical - are they shopping, transacting, or researching? These insights should directly shape navigation decisions.
The usage context significantly impacts navigation requirements. A retail app shopper has fundamentally different needs from someone checking financial data. Navigation should reflect these distinct scenarios with customized, predictable pathways.
Prioritizing Information Architecture
Logical content organization forms the foundation of effective navigation. Related information should group naturally, following user mental models. Establishing clear content relationships through thoughtful taxonomy helps users intuitively understand platform structure.
Navigation should mirror this organization, making connections between sections immediately apparent. This structured approach promotes efficiency and satisfaction throughout the user experience.
Leveraging Visual Hierarchy and Aesthetics
Strategic visual cues guide users through navigation pathways. Varied typographic treatments, color contrast, and spacing help emphasize important navigation elements. Aesthetically pleasing, intuitive designs make navigation feel effortless rather than frustrating.
Implementing Effective Mobile-Specific Design Patterns
Mobile interfaces demand specialized navigation solutions. Patterns like collapsible menus, tab bars, and bottom navigation have proven effective for small-screen usability. The appropriate pattern depends on content structure and user needs - extensive content benefits from hidden menus, while apps with few core functions work well with persistent navigation bars.
Testing and Iterating on Navigation Design
Rigorous testing with real users provides invaluable navigation insights. Observing where users encounter difficulties reveals opportunities for refinement. Behavior analysis helps identify which navigation elements perform well and which need adjustment.
Ensuring Seamless Transitions and Feedback
Smooth screen transitions and clear interaction feedback significantly enhance usability. Purposeful animations and visual responses reassure users that their actions have registered. This transparency in system behavior builds confidence and reduces errors.
Optimizing for Mobile-First Design Principles

Understanding the Mobile-First Mindset
True mobile-first design represents more than responsive layouts - it's a fundamental prioritization of mobile constraints from the outset. This approach guarantees core content and functions remain accessible even on the smallest displays. The discipline imposed by mobile limitations often yields cleaner, more focused designs that work well across all devices.
The mobile-first philosophy forces designers to simplify and prioritize, resulting in interfaces that communicate more effectively regardless of screen size.
Prioritizing Core Functionality
Mobile-first means identifying and perfecting essential features before considering enhancements. Developers must rigorously evaluate each element's necessity, ensuring nothing interferes with primary user goals. This focused approach frequently yields performance benefits like faster loading and reduced data usage.
Responsive Design Strategies
Fluid responsive techniques ensure consistent experiences across device spectra. Careful use of viewport-relative units and media queries creates seamless transitions between screen sizes. Responsive implementation maintains usability regardless of access device.
User Experience (UX) Optimization
Mobile UX demands particular attention to interaction design. Simplified navigation, appropriately sized touch targets, and streamlined layouts are non-negotiable for mobile usability. Performance optimization remains equally critical - slow mobile experiences drive users away regardless of design quality.
Measuring and Iterating for Continuous Improvement
Defining the Scope of Measurement
Effective measurement begins with clearly delineating which aspects require evaluation. Establishing relevant key performance indicators keeps analysis focused and actionable. Precise KPI definition ensures measurement aligns directly with organizational objectives. Overly broad scopes generate noise rather than insight.
For engagement-focused goals, meaningful metrics might include session duration, page depth, and retention rates. This targeted approach enables specific, impactful optimizations.
Establishing Baseline Metrics
Documenting current performance provides essential context for improvement assessment. Comprehensive baseline data forms the reference point for evaluating enhancement effectiveness. Collecting data across representative timeframes reveals existing patterns and normal performance ranges.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Selecting metrics that correlate directly with desired outcomes is crucial. Satisfaction improvements might track survey scores, support volume, and repeat usage. Proper KPI selection ensures measurement efforts focus on what truly matters.
Developing a Measurement Plan
A detailed measurement blueprint specifies data sources, collection methods, and analysis schedules. Comprehensive planning guarantees consistent, reliable data for informed decision-making. The plan should include provisions for data security and accommodate adjustments as needed.
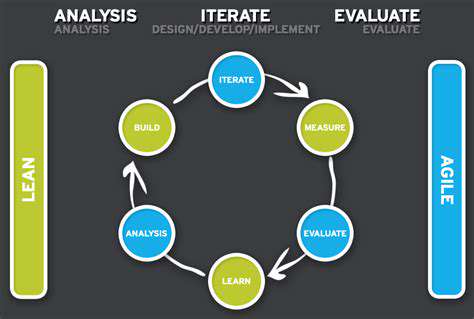
Implementing Iterative Changes
Gradual modifications based on data insights typically outperform wholesale redesigns. Smaller, measured changes allow precise impact assessment and minimize disruption. Continuous monitoring enables timely refinements to optimization strategies.
Analyzing Data and Identifying Trends
Regular data examination reveals meaningful patterns and opportunities. Consistent analysis surfaces insights that might otherwise remain hidden. Data visualization tools can transform raw numbers into actionable intelligence.
Refining the Process
Data-driven adjustments should continuously enhance operations. Ongoing refinement based on empirical evidence ensures sustained improvement. Regular evaluation catches emerging issues before they significantly impact performance.