Key Game Mechanics for Enhanced Engagement
Core Loop Mechanics
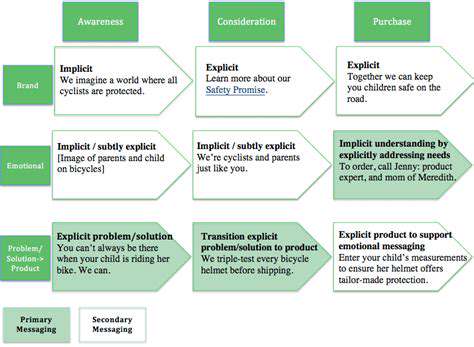
A well-designed mobile game, or in this case, a gamified shopping experience, hinges on a compelling core loop. This loop, a cycle of actions and rewards, must be intuitive and engaging for users. The core loop should clearly define the actions a user needs to take (e.g., browsing products, completing a purchase, earning loyalty points), the rewards they receive (e.g., discounts, exclusive access, points for future rewards), and the progression they experience. A user should feel they are moving forward and achieving something tangible as they engage with the gamified shopping experience.
Progressive Rewards and Challenges
Implementing a progressive reward system is crucial for sustained user engagement. This involves providing rewards that increase in value as users progress through the game's challenges. For example, early-level rewards could be small discounts or points, while higher-level rewards could be exclusive merchandise, early access to sales, or VIP treatment. The challenges themselves should be appropriately scaled, not overly difficult to discourage engagement, but not so easy as to make the rewards feel insignificant.
Clear milestones and achievable goals are paramount to keeping users motivated. Knowing that they are progressing and getting closer to significant rewards encourages continued participation and investment.
Leaderboards and Social Comparison
Integrating leaderboards and social comparison elements can drive healthy competition and encourage users to strive for better scores or achievements. For example, users could compete to earn the most points, collect the rarest items, or complete challenges faster than their friends or other players. However, it's essential to strike a balance, as excessive focus on competition can sometimes deter some users.
Personalized Experiences
Gamified shopping experiences should adapt and respond to individual user behavior. Personalization can manifest in various ways, such as tailored recommendations based on past purchases, dynamic challenges aligned with user preferences, and personalized rewards that cater to individual needs. By understanding user preferences and adapting the experience accordingly, businesses can create a more engaging and rewarding experience for each individual shopper.
Feedback Loops and Transparency
Providing immediate and clear feedback is crucial for maintaining user engagement in a gamified shopping experience. When users complete an action, they should receive instant confirmation or notification of their progress. Transparency about how points are earned, rewards are awarded, and leaderboards are calculated helps build trust and encourages continued participation. If users understand the system and how they can improve, they are more likely to engage.


Measuring Success and Iterating for Improvement
Defining Success Metrics
Establishing clear and measurable success metrics is crucial for any project or initiative. These metrics should be directly tied to the project's goals, allowing for a quantifiable assessment of progress. Without well-defined metrics, it's difficult to objectively evaluate the effectiveness of strategies and make informed decisions about improvements. Aligning metrics with overarching business objectives ensures that the project contributes meaningfully to the overall organization's success.
These metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This ensures that the targets are realistic and achievable within the allocated timeframe. Implementing this structured approach guarantees that progress can be tracked accurately and that adjustments can be made as needed.
Analyzing Data and Identifying Trends
Regular data analysis is essential to understanding patterns and trends. This process helps uncover insights that can guide decision-making and inform iterative improvements. By meticulously examining collected data, we can identify areas of strength and weakness, enabling us to make informed choices to optimize outcomes.
Tools and technologies for data visualization can play a pivotal role in this process. They allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the collected data, highlighting trends and outliers that might be missed in raw data. This visual representation facilitates more effective communication of findings to stakeholders.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
Analyzing data and identifying trends often reveals areas where the process or strategy could be improved. Thorough examination of the collected data allows for a critical assessment of the effectiveness of different elements within the project. This process should be proactive, not reactive, to ensure ongoing optimization and continuous improvement.
By identifying these areas, we can focus efforts on targeted improvements, leading to more efficient strategies and a higher likelihood of achieving desired outcomes. This proactive approach fosters a culture of continuous enhancement, driving progress toward optimal performance.
Developing and Implementing Iterative Solutions
Based on the analysis of data and identification of improvement areas, the next step is the development of iterative solutions. This involves creating and testing different approaches to address the identified challenges. This iterative approach allows for flexibility and adaptability, enabling the team to adjust strategies in response to emerging data and feedback.
These solutions should be tested in a controlled environment whenever possible. This allows for a more controlled evaluation of the efficacy of different approaches, reducing the potential for unintended consequences. This process ensures that resources are allocated wisely and that the desired outcome can be achieved.
Monitoring Progress and Evaluating Results
Continuously monitoring progress and evaluating results is vital for ensuring that improvements are effective and have the intended impact. This process involves tracking key metrics against the established goals and benchmarks. This allows for a real-time assessment of the success of implemented changes. Regular monitoring provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the strategies and allows for timely course corrections.
Regular reporting on progress is essential for transparency and accountability. This ensures that stakeholders are informed about the project's status and that progress can be evaluated with a collective understanding.
Implementing Feedback Loops
Implementing feedback loops is critical for continuous improvement. This involves actively soliciting feedback from stakeholders, customers, or team members. This feedback can identify areas where the processes or strategies can be enhanced to better meet the needs of the project's intended audience.
Integrating feedback loops into the project lifecycle is crucial. It allows for a dynamic and adaptable approach to problem-solving. Collecting and analyzing feedback allows for a highly responsive approach to change, ensuring that the project stays relevant and effective.
Adapting Strategies Based on Results
The final step in the iterative process is adapting strategies based on the results obtained. This involves adjusting approaches based on the feedback collected and the observed results. This enables the team to refine strategies and optimize their effectiveness over time.
Adapting strategies is an essential part of the process because it ensures that the project remains aligned with the evolving needs and conditions. This responsive approach is key to long-term success and sustainability.