Measuring Success and Iterating for Improvement
Defining Success Metrics
Success in any endeavor, whether personal or professional, necessitates a clear definition of what constitutes a successful outcome. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that objectively measure progress toward the desired goals. Without clearly defined metrics, it's difficult to track progress and make informed decisions about adjustments and improvements. A well-defined metric system allows for continuous monitoring and evaluation, providing valuable insights into areas needing attention.
The definition of success should be specific and measurable. Instead of a vague goal like increase sales, a more effective metric would be increase sales by 15% in the next quarter. This specificity allows for the creation of a roadmap toward success, ensuring that every step taken aligns with the desired outcome.
Analyzing Data and Identifying Trends
Once the metrics are established, the next crucial step is to meticulously analyze the data collected. This involves identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that might provide insights into the factors driving success or failure. Careful examination of this data helps in understanding the dynamics at play and in making well-informed decisions. A detailed analysis helps to understand what aspects are working effectively and where improvements are needed.
Tools and software dedicated to data analysis can be incredibly useful in this process. They can help to visualize trends and patterns, allowing for faster and more efficient identification of critical information within large datasets. This data-driven approach empowers decision-making, leading to more effective strategies.
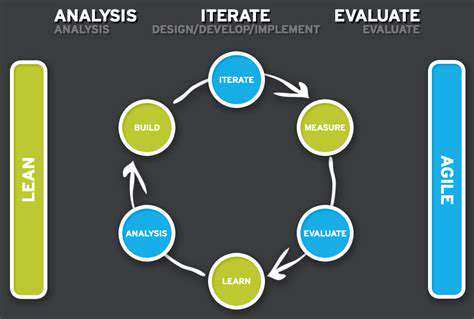
Iterative Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of success. Iterative strategies allow for adaptation and refinement based on ongoing analysis of data and feedback. This involves regularly evaluating the current approach and making necessary adjustments to optimize performance and achieve desired outcomes.
By incorporating feedback from various sources, including clients, colleagues, and internal teams, organizations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of what works and what needs improvement. This cycle of evaluation, adaptation, and refinement is essential for achieving sustainable growth and success.
Implementing Changes and Monitoring Results
Implementing the changes identified during the analysis phase is a critical step in the iterative process. This often involves adjustments to processes, strategies, or resources. Thorough planning and communication are essential for a smooth implementation process. Clear communication ensures that all stakeholders understand the changes and their rationale. This process requires careful consideration of potential impacts and risks associated with the changes.
Learning from Failures and Adapting
Failures are inevitable parts of any iterative process. Learning from failures is crucial for adapting and improving strategies in the future. Analyzing what went wrong and why is essential for preventing similar mistakes in the future. Taking the time to understand the root causes of failures allows for the creation of more resilient and effective strategies.
A key element of this learning process is a willingness to embrace failures as opportunities for growth and development. Openness to feedback and a willingness to experiment are essential for continuous improvement.